Full Screen
Chemical Bonds
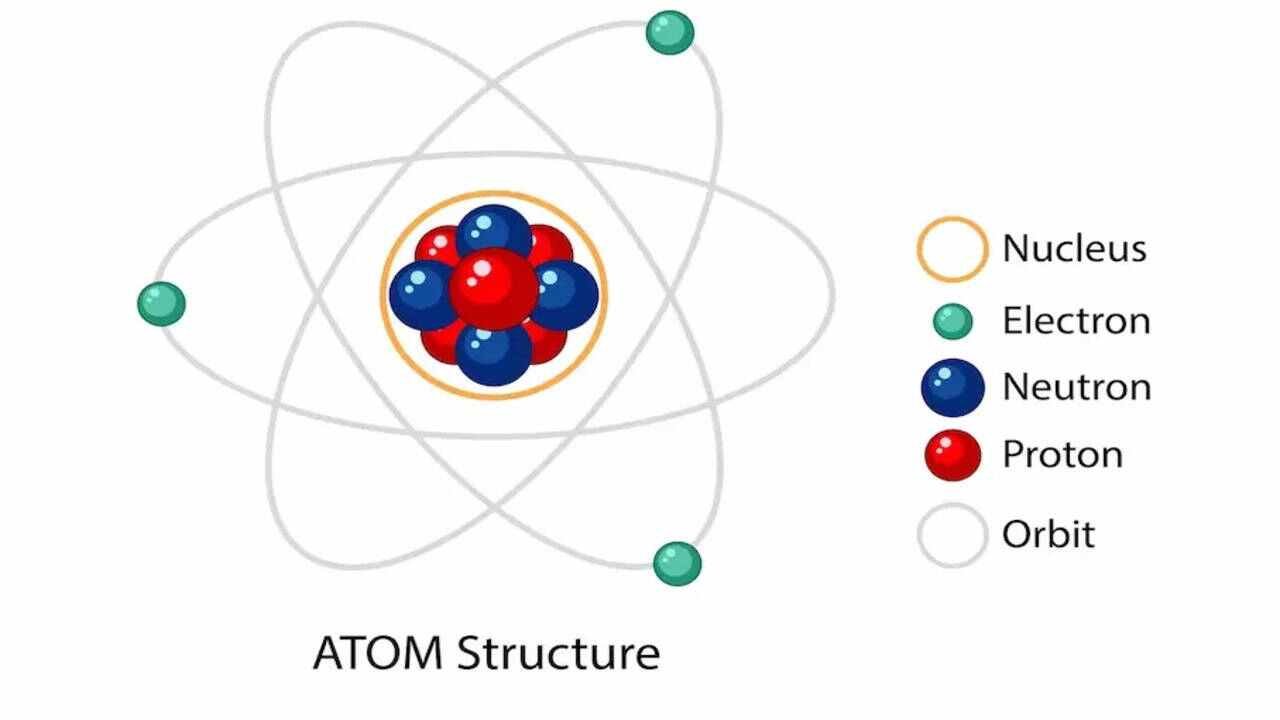
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together in molecules. There are two main types of chemical bonds: ionic and covalent. In an ionic bond, one atom transfers electrons to another atom, resulting in positive and negative ions that attract each other. This type of bond often forms between metals and nonmetals. In contrast, a covalent bond occurs when atoms share electrons, usually between nonmetals. These shared electrons help both atoms achieve a stable configuration. Understanding chemical bonds is essential because they determine the properties of substances, such as their melting points, conductivity, and reactivity.
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together in molecules
There are two main types of chemical bonds: ionic and covalent.